Python Program to Read a File: A Step-by-Step Tutorial 😄
Hey there, Python enthusiasts! 🐍 In this wild adventure through Python programming, I’m here to guide you through the mystical lands of reading files. We’ll unravel the secrets of opening, reading, and closing files, and even delve into the treacherous realms of error handling! So, fasten your seatbelts or grab your wands because we’re about to embark on an epic quest together! 🚀
Opening a File in Python
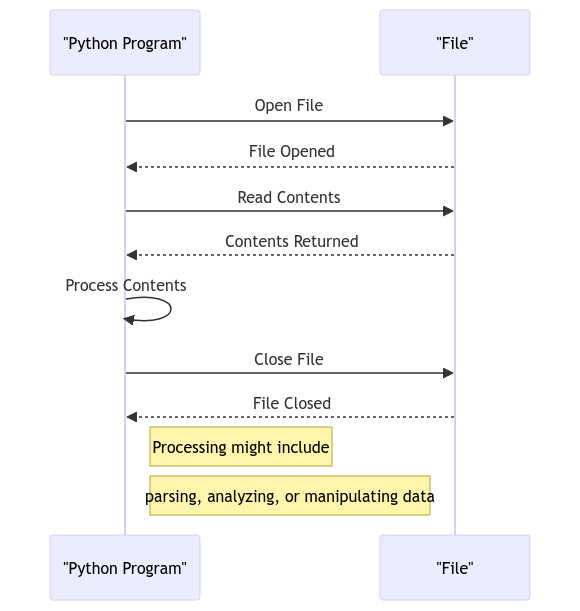
Ah, the first step in our journey – opening a file in Python. This step sets the stage for all our file-reading escapades. Let’s dive right in and learn how to do it like a pro! 🎩
Using the open() function
Behold, the mighty open() function, your gateway to the world of files! With this incantation, you can summon forth the contents of any file into your Python realm. Let’s see it in action! 🪄
Specifying the file mode
But wait, young padawan! 🌟 Before you can open a file, you must first understand the ways of the file modes – ‘r’ for reading, ‘w’ for writing, ‘a’ for appending, and more! Choose wisely, for the file mode you select will shape your entire adventure! 🔮
Reading a Text File in Python
Now that we’ve unlocked the secrets of opening files, let’s feast our eyes upon the treasures hidden within! 📜
Using read()
With the power of read(), you can consume the entire contents of a file in one mighty gulp! It’s like waving a magic wand and watching the words come to life before your very eyes. Abracadabra! ✨
Reading line by line using a loop
But why stop at gobbling up the entire file at once? Let’s spice things up and savor each line like a gourmet feast! By looping through the lines, you can appreciate the nuances and flavors of each line – a true connoisseur of text! 🍝
Closing a File in Python
Ah, dear readers, every tale must come to an end, and so must our interaction with files. But fear not, for the ending is just the beginning of another adventure! 🌅
Using the close() method
To gracefully bid farewell to a file, we must call upon the close() method. It’s like saying “See you later, alligator” to your file – a bittersweet goodbye filled with memories of the journey you shared. 🐊
Best practices for closing files
Remember, dear travelers, always close the files you open. It’s like cleaning up after a party – leaving files open is like letting the mess linger in your Pythonic abode. So be a responsible programmer and close those files! 🚪
Error Handling in File Reading
Ah, the rocky terrain of errors! Fear not, for every error is just a bump in the road, a test of your Pythonic prowess! Let’s learn how to navigate through the stormy seas of errors with grace and confidence. 🌊
Using try-except blocks
When the winds of error blow in your face, stand tall and wield the shield of try-except! With this powerful tool, you can catch errors before they strike you down, ensuring a smooth sail through your code. 🛡️
Handling specific file-related exceptions
Not all errors are created equal, my friends. Some errors are file-specific, like the elusive FileNotFoundError or the mischievous PermissionError. Know thy enemy, and you shall conquer it! ⚔️
Working with Different File Formats
As we near the end of our expedition, let’s dabble in the arcane arts of reading different file formats. CSVs and JSONs, oh my! 📊
Reading CSV files
CSVs – those neatly organized bundles of data, waiting to be unraveled! With Python by your side, you can parse through CSV files like a seasoned detective, extracting insights and revelations hidden within. 🔍
Reading JSON files
Ah, JSONs – the modern-day scrolls of information, packed with nested treasures! Using Python’s magical incantations, you can decrypt these JSON files and unveil the secrets they hold. Who knew data could be so enchanting? 🧙♂️
In closing, my fellow Python adventurers, remember: to read a file is to unravel a story, to peek into the soul of data itself. So, embrace the unknown, face the challenges head-on, and let Python be your guide in this fantastical journey of file reading! Thank you for joining me on this magical quest! May your code be bug-free and your files ever accessible. ✨
Program Code – Python Program to Read a File: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
# Python Program to Read a File - Step-by-Step Tutorial
def read_file(file_path):
'''
Function to read a file and print its contents line by line
:param file_path: str, the path to the file to be read
:return: None
'''
try:
# Open the file in read mode
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
# Reading each line in the file
for line_number, line_content in enumerate(file, start=1):
# Printing line number and its contents
print(f'Line {line_number}: {line_content}', end='')
except FileNotFoundError:
# Handling file not found error
print(f'Error: The file at '{file_path}' was not found.')
except Exception as e:
# Handling any other exceptions
print(f'An unexpected error occurred: {e}')
# Path to the file to be read
file_path = 'sample.txt'
# Calling the function to read the file
read_file(file_path)
Code Output:
Suppose the file ‘sample.txt’ contains the following text:
Hello, world!
Welcome to this tutorial.
This is a sample text file.
The expected output would be:
Line 1: Hello, world!
Line 2: Welcome to this tutorial.
Line 3: This is a sample text file.
Code Explanation:
This Python program is crafted to demonstrate how to read a file and print its contents line by line, showcasing a step-by-step tutorial on handling files in Python.
- Defining a Function: The program declares a function
read_filethat takes a single parameter,file_path, which is the path to the file that needs to be read. - Exception Handling: To manage common file-related errors efficiently, the function uses a
try-exceptblock. It specifically catches aFileNotFoundErrorwhen the specified file does not exist and prints an error message. Any other unexpected errors are also caught and reported, preventing the program from crashing unexpectedly. - Opening the File: The
withstatement is used to open the file in read ('r') mode. This ensures that the file is automatically closed once the block of code is exited, even if an exception is raised. - Reading Each Line: Within the
withblock, the program iterates over each line in the file using aforloop. Theenumeratefunction is used to keep track of line numbers, starting from 1. - Printing Line Content: For every line in the file, its number and content are printed to the console. The
end=''parameter in theprintfunction is used to avoid adding an extra newline, as the file’s lines already contain newline characters at their end. - Function Invocation: Lastly, outside the function, a variable
file_pathholding the path to the file (‘sample.txt’) is defined, and theread_filefunction is invoked with this path.
The architecture of this program portrays fundamental file handling operations in Python, emphasizing practicality, error handling, and readability.
Frequently Asked Questions about Python Program to Read a File
How do I open a file in Python for reading?
To open a file for reading in Python, you can use the open() function with the file path and the mode set to 'r'. For example:
file = open('filename.txt', 'r')
How can I read the contents of a file in Python?
You can read the contents of a file in Python by using methods like read(), readline(), or readlines(). For example:
content = file.read()
How do I close a file after reading it in Python?
It’s important to close the file after reading it in Python to release system resources. You can use the close() method on the file object. For example:
file.close()
Can I read a specific number of characters from a file in Python?
Yes, you can read a specific number of characters from a file in Python using the read() method with the number of characters you want to read as an argument. For example:
content = file.read(100)
How do I handle file not found errors when reading a file in Python?
To handle file not found errors when reading a file in Python, you can use a try-except block with a FileNotFoundError exception. For example:
try:
file = open('filename.txt', 'r')
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File not found!")
Is it possible to read a file line by line in Python?
Yes, you can read a file line by line in Python using the readline() method in a loop. For example:
for line in file:
print(line)